Technical Specifications for American Passport Size Photos: Complete DS-160 Requirements Guide
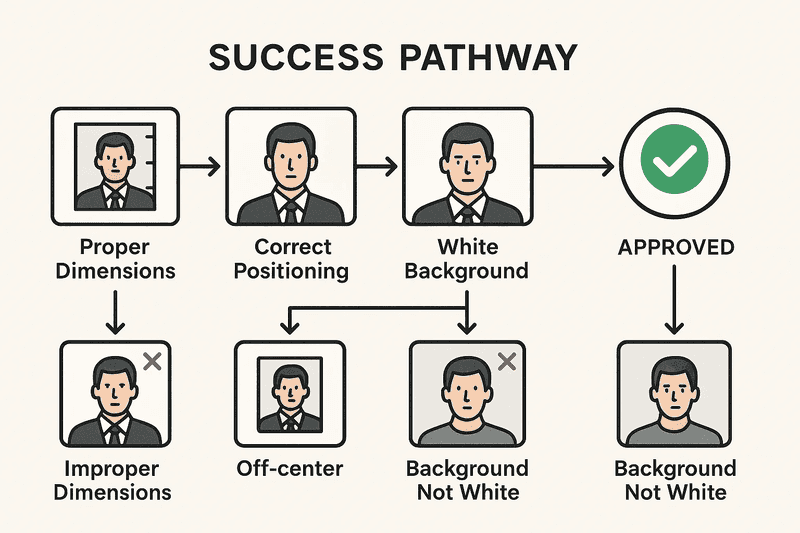
The required dimensions for US passport and visa photos
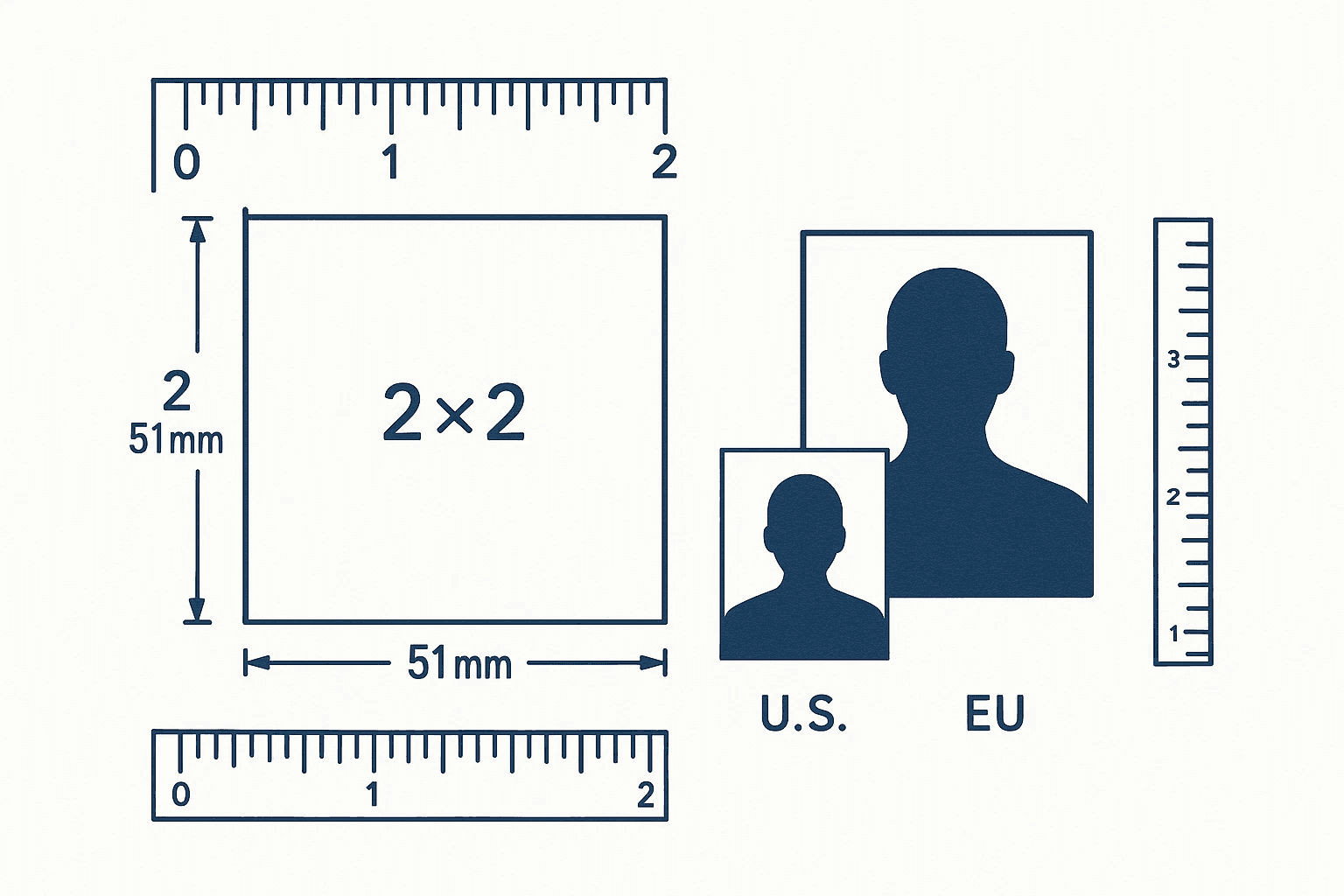
The United States maintains stringent biometric standards for passport photos and visa photos that directly impact application success rates. The fundamental requirement of 2x2 inches (51x51mm) represents more than a simple measurement—it establishes the foundation for facial recognition systems used by the Department of State. This square format differs from international standards, making US passport and visa photos unique in their technical specifications. Digital submissions require 600x600 to 1200x1200 pixels at 300 DPI, maintaining the same 1:1 aspect ratio while ensuring sufficient resolution for biometric processing.
The distinction between physical and digital specifications often creates confusion among applicants. When preparing new visa photos or passport photos, understanding that 2x2 inches equals 600x600 pixels at standard 300 DPI resolution prevents costly rejection delays. The State Department's automated verification systems scan every photo submission against these precise parameters, with rejection rates exceeding 56% for positioning errors alone.
Technical pixel dimensions and DPI requirements decoded
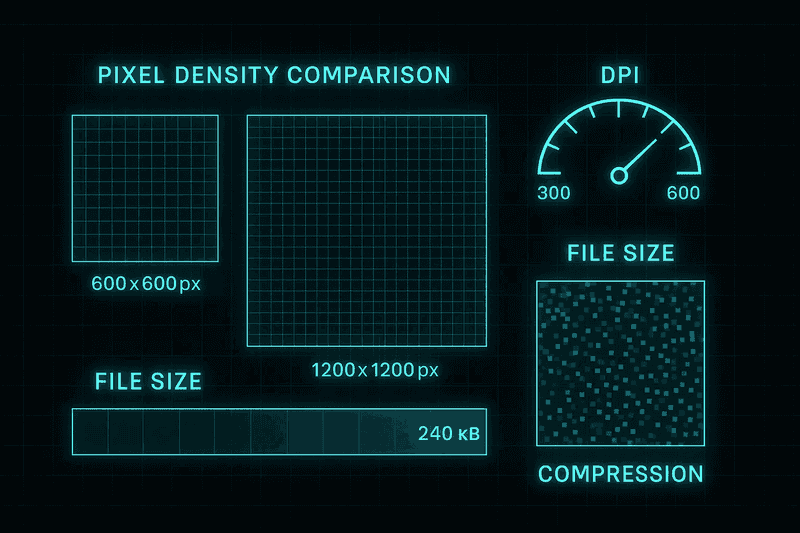
Digital passport and visa photos demand specific technical compliance beyond basic sizing. The minimum 600x600 pixel requirement ensures adequate facial detail capture, while the 1200x1200 maximum prevents unnecessary file bloat. These specifications translate to exact DPI requirements: 300 DPI for standard quality and up to 600 DPI for enhanced resolution. File compression must not exceed a 20:1 ratio, preserving biometric markers essential for identity verification.
The DS-160 form enforces strict JPEG format requirements with maximum file sizes of 240KB. This constraint requires careful balance between image quality and compression. Professional photographers recommend capturing at 1200x1200 pixels initially, then optimizing compression settings to meet file size limits while maintaining clarity. The sRGB color space standard ensures consistent color reproduction across different display systems used by consular officials.
Understanding these technical parameters becomes crucial when converting existing photos. A photo captured at 4000x4000 pixels must be precisely cropped and resized to maintain the required head-to-image ratio of 50-69%. The eye level positioning between 56-69% from the bottom edge serves as a critical alignment marker for facial recognition algorithms.
iPhone photography settings for compliant passport photos
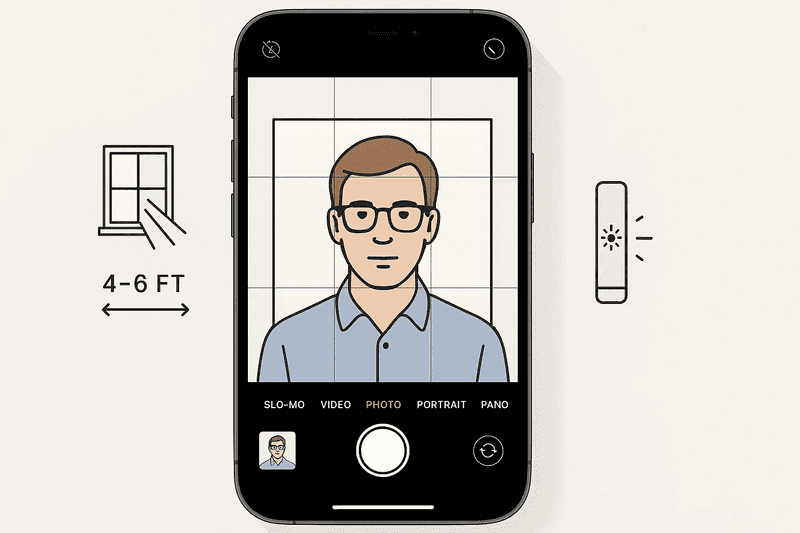
Modern iPhone cameras exceed the technical requirements for passport photos when configured correctly. Disable the mirror front camera setting and utilize the rear camera exclusively, positioning the device 4-6 feet from the subject. The iPhone's grid overlay feature assists with proper head centering and composition. Set the camera to capture in HEIF or highest quality JPEG format, ensuring files retain sufficient detail for the required 300 DPI output resolution.
Natural window lighting produces optimal results, eliminating harsh shadows that cause automatic rejections. Position the subject facing the light source at a 30-degree angle, avoiding direct sunlight that creates overexposure. The iPhone's exposure adjustment slider helps balance lighting across facial features. White balance settings should remain on automatic to preserve natural skin tones required by biometric systems.
Creating the proper plain white or off white background requires careful positioning. A seamless white wall works best, positioned at least 12 inches behind the subject to prevent shadow casting. The iPhone's Portrait mode should remain disabled, as artificial background blur violates passport photo requirements. Multiple shots increase success probability, with professional services recommending capturing 10-15 images to select the optimal frame.
Converting iPhone photos to the exact 2x2 format involves using the built-in Photos app editor to crop to 1:1 aspect ratio, then utilizing specialized apps or online tools to resize to precise pixel dimensions. The final step requires saving in JPEG format with appropriate compression to meet the 240KB file size limit for DS-160 uploads.
Common rejection triggers and compliance violations
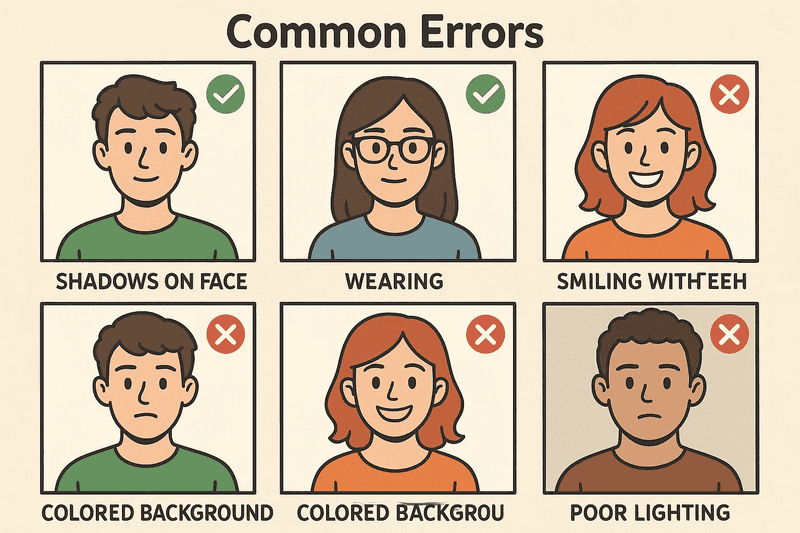
Technical analysis of 10,083 rejected photos reveals systematic patterns in non-compliance. Incorrect head positioning accounts for the majority of rejections, with heads too large or small relative to frame dimensions. The required neutral facial expression proves challenging, as even slight smiles can trigger rejection if teeth show or facial geometry changes significantly. Eyes must remain fully open and clearly visible, with no hair obstruction or shadowing.
Lighting violations represent the second-highest rejection category. Overexposed photos lose critical facial detail, while underexposed images fail contrast requirements. Shadows across the face, particularly from overhead lighting or hat or head covering edges, result in immediate rejection. The background must maintain consistent white or off-white coloring without gradients or variations that suggest environmental shadows.
The prohibition on eyeglasses since November 2016 continues causing rejections for applicants unaware of the policy change. Medical exemptions require signed documentation and still mandate no glare or frame obstruction. Similarly, applicants cannot wear a hat or head covering except for documented religious or medical reasons. Even permitted religious head coverings must not cast shadows or obscure the hairline completely.
Digital manipulation detection systems identify and reject photos with applied filters, beauty modes, or retouching. Red-eye correction, blemish removal, and skin smoothing all qualify as unacceptable photos under current guidelines. The State Department provides visual guides showing acceptable and unacceptable photos to clarify these requirements.
Religious exemptions and medical accommodation protocols
Religious head coverings receive special consideration under State Department regulations. Daily-worn religious attire including hijabs, turbans, and yarmulkes qualify for exemption with signed statements. The head covering must not obscure facial features or cast shadows that interfere with biometric scanning. Full-face visibility remains mandatory, making niqabs and burkas incompatible with passport photo requirements.
Medical exemptions for glasses or head coverings require physician documentation specifying the medical necessity. Recent eye surgery or conditions preventing glass removal temporarily qualify for exemption. The documentation must accompany the photo submission, whether digital or physical. Medical head coverings follow similar visibility rules as religious exemptions, ensuring complete facial feature exposure.
Disability accommodations extend beyond head covering exemptions. Hearing aids and medical devices worn daily appear in photos without restriction. Elderly applicants over 75 and those with mobility limitations can request special processing arrangements, though biometric requirements remain unchanged. Children under two receive relaxed expression requirements, acknowledging the difficulty of maintaining neutral expressions in infants.
Print specifications and paper quality standards
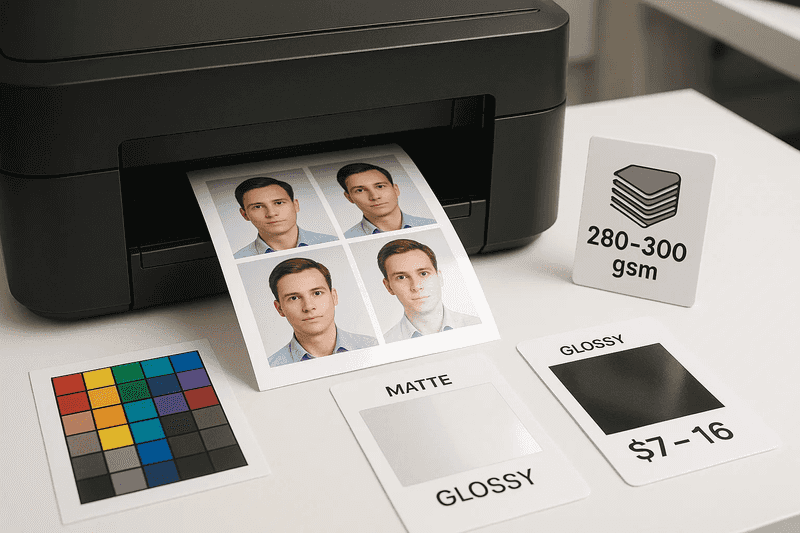
Physical passport photos demand specific printing parameters beyond dimensional accuracy. Photo-quality paper in matte or glossy finish ensures durability and color accuracy. Standard photo paper weight of 280-300 GSM prevents curling and damage during handling. Home printing requires photo-specific paper and calibrated color settings to match professional standards.
Professional printing services guarantee compliance but vary significantly in cost. Pharmacy chains charge $14.99-$15.99 for passport photo services, while discount retailers offer options starting at $7.44. Online services provide digital verification before printing, reducing rejection risks. The investment in professional printing often prevents costly resubmission delays.
Print resolution must maintain 300 DPI minimum to preserve facial detail clarity. Lower resolutions create pixelation visible to both automated systems and human reviewers. Color accuracy proves critical, as skin tone variations can trigger biometric matching failures. Printers should use photo-specific color profiles rather than document settings to ensure accurate reproduction.

DS-160 upload procedures and digital format requirements
The US visa photo checker tool validates photos against all visa photo requirements before submission, preventing common rejection scenarios. This pre-screening identifies issues with head positioning, background consistency, and technical specifications that automated systems flag. Using validation tools before final submission significantly improves first-attempt success rates.
Differences between passport photos and visa photo standards
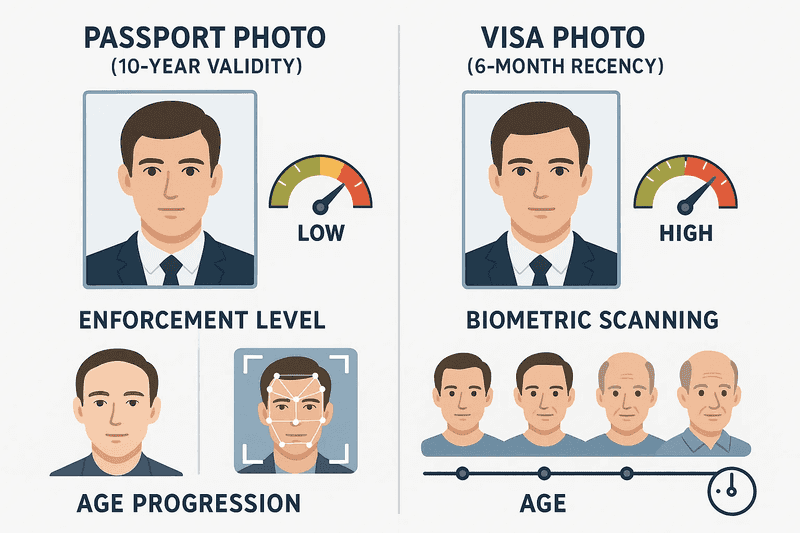
While US passport and visa photos share identical 2x2 inch dimensions and technical specifications, enforcement and usage patterns differ substantially. Passport photos serve for document issuance lasting 10 years, while visa photos support temporary travel authorizations. This temporal difference affects recency requirements, with visa photos strictly enforced at six months versus passport photos' more flexible interpretation.
The question of using passport photos for visa applications receives qualified approval. Photos meeting all current visa photo requirements work regardless of original purpose. However, age limitations and appearance changes often necessitate new visa photos even when existing passport photos technically comply. Significant weight changes, facial hair modifications, or hairstyle alterations trigger new photo requirements.
Professional services versus DIY photo creation
Professional photo services offer compliance guarantees that DIY methods cannot match. Studios specializing in passport and visa photos understand subtle requirements like exact head positioning and background uniformity. Their controlled lighting environments eliminate shadow risks, while professional cameras capture superior detail compared to smartphones. The $15-20 investment often prevents multiple rejection cycles costing time and additional fees.
DIY photo creation succeeds with proper preparation and tools. Smartphone cameras meeting 12-megapixel specifications capture sufficient detail when properly configured. Online editing tools assist with cropping and background replacement, though manual adjustments risk introducing non-compliance. The key advantage remains cost savings and convenience, particularly for tech-savvy applicants comfortable with photo editing.
Success rates favor professional services, particularly for first-time applicants unfamiliar with requirements. DIY methods work best for renewal applications where previous photos provide reference templates. The decision ultimately balances cost considerations against rejection risk tolerance and available time for potential resubmissions.

Conclusion: Ensuring first-attempt photo approval